Common Hoof Problems and How to Fix Them
Common hoof problems in horses include thrush, abscesses, white line disease, laminitis, and hoof cracks. You can usually manage these with regular hoof care, a balanced diet, and help from a farrier or vet when needed. Maintain your horse’s hooves by cleaning, trimming, and nourishing them regularly. This keeps them healthy and prevents problems.
Importance of Healthy Hooves
Healthy hooves are essential for a horse’s well-being and performance. They support the horse’s weight, absorb impact, and allow for proper movement. Healthy hooves help avoid issues that can impact a horse’s comfort when moving. Regular care and attention to the hooves ensure they stay strong and functional. Healthy hooves contribute to a horse’s overall comfort and long-term soundness.
Common Hoof Problems
Thrush
Thrush in horses is a bacterial infection that typically affects the frog of the hoof. It is characterised by a foul odour and, if left untreated, can lead to lameness. Damp or dirty environments often cause the condition. These places let bacteria thrive in the hoof.
Symptoms:
- Foul smell emanating from the hooves. Black, mushy areas in the frog. The frog shows lameness or sensitivity when pressure is applied.
Causes:
- Wet or muddy environments. Lack of regular hoof cleaning. Poor stable hygiene or bedding.
Treatment:
- Clean hooves daily to remove dirt and debris. Apply antiseptic or thrush-specific treatments. Keep hooves dry and ensure a clean and dry environment. In severe cases, consult a farrier for trimming and further treatment.
2. Laminitis
Laminitis is a painful condition. It affects the hooves and causes inflammation in the tissues that connect the hoof to the bone. It is often caused by overeating rich food, sudden diet changes, or metabolic issues. If not treated quickly, it can lead to permanent damage to the hooves.
Symptoms:
- Sudden and severe lameness, particularly in the front hooves.
- Heat in the hooves, especially near the coronet band.
- “Rocking horse” stance due to pain and pressure.
- Reluctance to walk or shift weight.
Causes:
- Overfeeding on lush pasture, especially high-sugar grasses. Endocrine disorders like Cushing’s disease or insulin resistance. Physical trauma or excessive weight-bearing on one limb.
Treatment:
- Immediate veterinary attention is essential for managing the condition. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as phenylbutazone (bute) to manage pain and swelling. Rest and soft bedding to reduce pressure on the hooves. In severe cases, corrective shoeing, medical intervention, or even surgery may be required.
3. Hoof Bruise
A hoof bruise is an injury to the soft tissues inside a horse’s hoof. It causes internal bleeding and pain. It often happens when a hoof hits something hard or sharp, like a stone or rough ground. This can damage soft parts, including the sole, frog, or hoof capsule. Bruises vary in severity.
Mild ones may cause temporary lameness. More serious bruises can damage deeper tissues and lead to lasting pain. If left untreated, hoof bruises can develop into infections or abscesses. Finding problems early and getting the right care is crucial. This helps prevent complications and supports proper healing.
Symptoms:
- Lameness or limping, especially on hard ground.
- Heat and swelling in the affected hoof.
- The hoof feels tender when pressed.
Causes:
- Stepping on rocks, nails, or other hard objects.
- Unbalanced or overgrown hooves cause pressure.
- Poor-fitting shoes or a rough surface.
Treatment:
- Rest the horse and avoid walking on hard or rocky ground. Soak the hoof in warm water with Epsom salts to reduce swelling. Apply a hoof pad or boot to cushion the bruise. Consult a farrier to correct any hoof imbalances or trimming issues.
4. Abscess
An abscess in the hoof happens when bacteria enter through a crack, puncture, or injury. This leads to a pocket of pus forming. This condition leads to significant pain, lameness, and swelling. If left untreated, an abscess can rupture, leading to infection and further complications.
Symptoms:
- Sudden and severe lameness.
- Heat and swelling in the affected hoof.
- Foul-smelling discharge if the abscess bursts.
- A visible hole or crack where the abscess may have originated.
Causes:
- Puncture wounds or cracks that allow bacteria to enter the hoof. Poor hoof care or lack of hygiene. Stepping on sharp objects, like nails, that puncture the hoof.
Treatment:
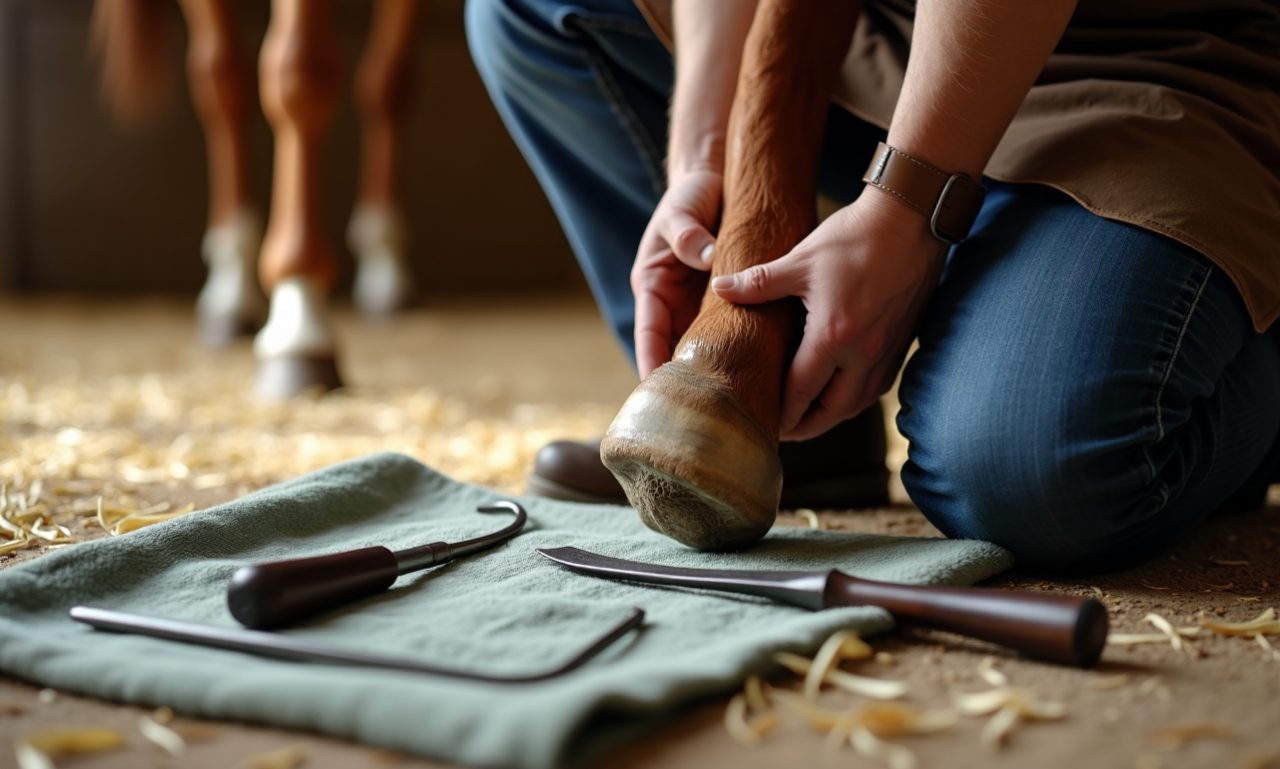
- Soak the hoof in warm Epsom salt baths to draw out the infection.
- Consult a farrier to drain the abscess or trim the affected area.
- Apply antiseptic to prevent further infection and keep the hoof clean.
- If the abscess is severe, a vet may need to administer antibiotics.
5. White Line Disease
White line disease (WLD), or “seedy toe,” affects horse hooves. It causes a gap between the hoof wall and the sole. This gap lets bacteria and fungi in. This can cause infection, pain, and even lameness. It often starts at the toe area of the hoof and can spread along the hoof wall if left untreated.
The exact cause of WLD isn’t always clear. It often relates to bad hoof care, filthy living spaces, and prolonged exposure to wet or muddy areas. Horses that are shod incorrectly or have damaged hooves are more likely to develop this condition. Horses with imbalanced hooves or weak hooves are also at a higher risk.
Symptoms:
- Separation of the hoof wall from the sole, often along the white line. A black, crumbly material around the affected area. The horse feels lameness or pain, especially when pressure is put on the hoof.
Causes:
- Poor hygiene or lack of cleaning. Wet and unsanitary conditions. Fungal or bacterial infections that invade the white line.
Treatment:
- Clean and disinfect the affected area regularly. A farrier will often trim away the affected tissue to prevent the infection from spreading. Antiseptic treatments or specialized products designed for WLD. Ensure the horse’s environment is kept dry and clean.
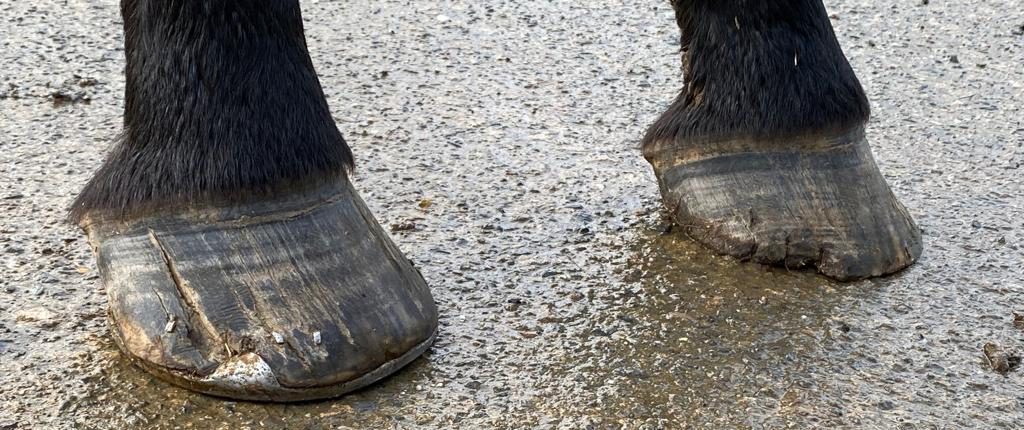
6. Hoof Cracks
Hoof cracks in horses can vary. They may be minor surface problems or more serious issues that lead to pain and lameness. They are commonly caused by an imbalanced hoof, improper trimming, or trauma to the hoof. Weather conditions like too much dryness or wetness can lead to hoof cracks. Poor nutrition, leading to weak hooves, is another factor that can make cracks more likely. If not treated, cracks can cause infections. Regular hoof care is key to preventing and managing them.
Symptoms:
- Visible cracks or splits in the hoof wall.
- Pain or lameness, particularly if the crack is deep.
- Swelling or infection around the crack.
Causes:
- Dry, brittle hooves due to lack of moisture.
- Trauma or pressure on the hoof.
- Poor hoof care or uneven trimming.
- Environmental factors such as extreme heat or dryness.
Treatment:
- Moisturize the hooves regularly with hoof conditioners or oils.
- Trim hooves regularly to prevent cracks from worsening.
- In some cases, the farrier may apply a patch or shoe to stabilise the crack.
- Keep the hoof clean to prevent infection.
7. Navicular Disease
Navicular disease is a degenerative issue. It impacts the navicular bone and nearby structures in the hoof. It often happens in horses that are overworked, poorly shaped, or get bad hoof care. The condition causes pain in the hooves. This leads to a long-term management process.
Symptoms:
- Chronic lameness, often in the front hooves.
- Short, choppy strides and reluctance to move.
- Sensitivity when pressure is applied to the heels of the hoof.
Causes:
- Poor hoof conformation or imbalanced trimming. Overwork or excessive stress on the hooves. Injury or trauma to the navicular bone.
Treatment:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs like phenylbutazone to manage pain.
- Specially designed shoes or pads to support the navicular bone.
- Rest and avoiding hard ground or excessive work.
- In severe cases, surgery or injections may be required.
8. Sheared Heels
Sheared heels occur when one side of the horse’s hoof grows higher than the other, causing imbalance. This condition is often a result of improper trimming or conformation issues. Over time, sheared heels can lead to pain, lameness, and further hoof problems.
Symptoms:
- Visible imbalance in the height of the heels. Lameness or discomfort when walking. Swelling or tenderness around the affected heels.
Causes:
- Uneven or incorrect trimming by the farrier. Hoof conformation issues. Improper exercise or environmental factors.
Treatment:
- Regular, correct trimming by an experienced farrier to restore balance. Special shoes or corrective trimming may be required. Close monitoring of the hooves to catch early signs of imbalance.
Conclusion
Taking care of your horse’s hooves is crucial for their health and well-being. Common hoof problems such as thrush, laminitis, abscesses, and cracks can cause pain and discomfort if left untreated. Regular cleaning, hoof inspections, and timely treatment can help prevent most hoof problems.
To keep your horse’s hooves healthy, focus on good hygiene. Make sure your horse has proper nutrition, too. Consult with a farrier or vet regularly. This can help you avoid many common problems. Detecting and treating hoof problems early is crucial. It helps manage issues well and stops them from getting worse.
A proactive approach to hoof care will keep your horse comfortable, active, and free from pain. Regular attention to hoof health is essential for a happy, healthy horse.
FAQS
How often should I clean my horse’s hooves?
You should clean your horse’s hooves at least once a day, especially before and after exercise. Regular cleaning removes dirt and debris, helping to prevent discomfort or injury. In some cases, cleaning 2-3 times a day may be needed, depending on your horse’s activity and environment.
Are there specific supplements that improve hoof health?
Some supplements can boost hoof health. Biotin, zinc, copper, and methionine are especially helpful. These nutrients support hoof strength and growth. Regular supplementation can help maintain healthy hooves over time.
What type of bedding helps reduce hoof problems?
Bedding that is dry and clean helps reduce hoof problems. Straw, shavings, or wood pellets are good choices as they keep the area comfortable. Avoid wet bedding, as too much moisture can cause issues like thrush.

Welcome to Sell Your Horse, a platform dedicated to connecting equestrians with each other, making horse buying and selling easier and more transparent. With a focus on technology and community-building. My mission is to help like-minded equestrians find the right connections, share knowledge, and build a trusted equine network.



















 Featured Listings
Featured Listings
 Adverts
Adverts
 Horses For Sale
Horses For Sale
 Tack & Equipment
Tack & Equipment
 Horseboxes & Trailers
Horseboxes & Trailers
 Equine Properties
Equine Properties
 4x4 Vehicles
4x4 Vehicles
 Horses For Loan
Horses For Loan
 Horses Wanted
Horses Wanted
 Stallions at Stud
Stallions at Stud
 Equine Services
Equine Services
 Riding Holidays
Riding Holidays
